In a world where Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing technology, AMD has boldly introduced its new Ryzen AI 300 series processors, also known as Strix Point. These processors integrate the XDNA2 NPU, specifically designed to enhance Copilot+ PC features.
Zen 5 and Zen 5c, the heart of the AMD Ryzen AI 300
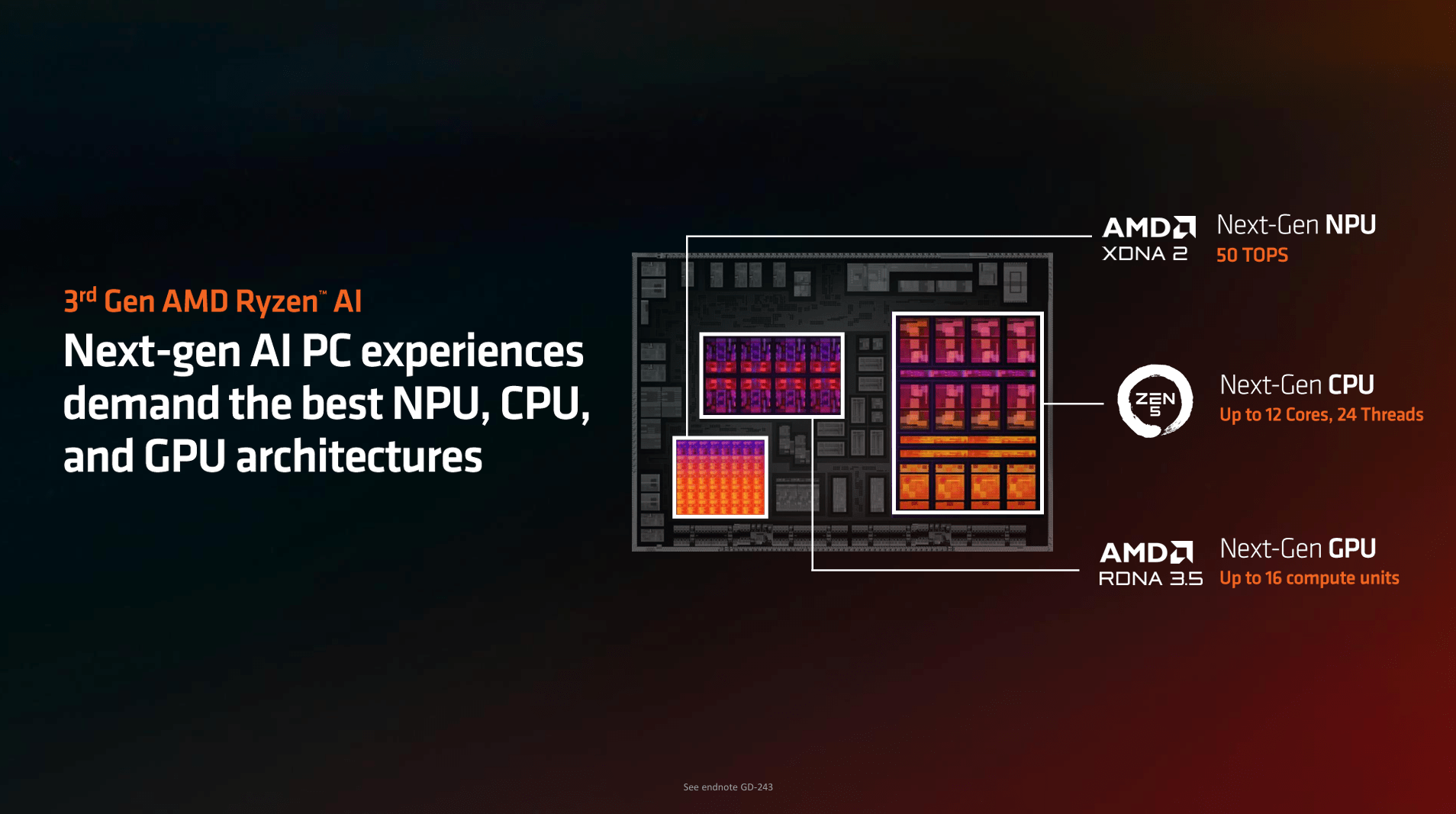
The Ryzen AI 300 series is built on AMD’s new Zen 5 architecture, marking a significant leap from previous generations. With up to 12 cores, the processors continue to excel in multitasking, one of AMD’s core strengths. Utilizing TSMC’s 4nm node, this architecture offers improved energy efficiency, making it more power-efficient.
A notable innovation is the combination of Zen 5 and Zen 5c cores within the same processor. The Zen 5 cores are designed for high-performance tasks, while the Zen 5c cores handle-less power-intensive operations. This hybrid approach balances processing power and energy efficiency, catering to demanding applications and everyday tasks.
Differences and Similarities between Zen 5 and Zen 5c
- Processing frequency: The Zen 5 cores in AMD’s Ryzen AI 300 series are optimized for higher processing frequencies, making them perfect for high-performance gaming or resource-intensive applications. In contrast, the Zen 5c cores run at lower frequencies to optimize power consumption, ideal for less demanding activities like background processes or mobile devices.
- IPC (Instructions Per Cycle): Despite operating at different frequencies, Zen 5 and Zen 5c cores share the same IPC (Instructions Per Cycle), meaning they perform equal work per clock cycle. This consistency ensures high efficiency and performance across both core types, regardless of the task.
The Zen 5c cores are specially designed for power efficiency, making them ideal for mobile devices where long battery life is critical.
It’s important to note that AMD’s approach with Zen 5/Zen 5c differs from Intel’s hybrid architecture, such as in Lunar Lake. While Intel’s hybrid approach involves distinct core types (performance vs. efficiency), AMD’s cores are fundamentally similar, with the primary difference being the operating frequency.
Features like Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) are preserved across all cores, ensuring high performance and multitasking capability, even at lower frequencies.
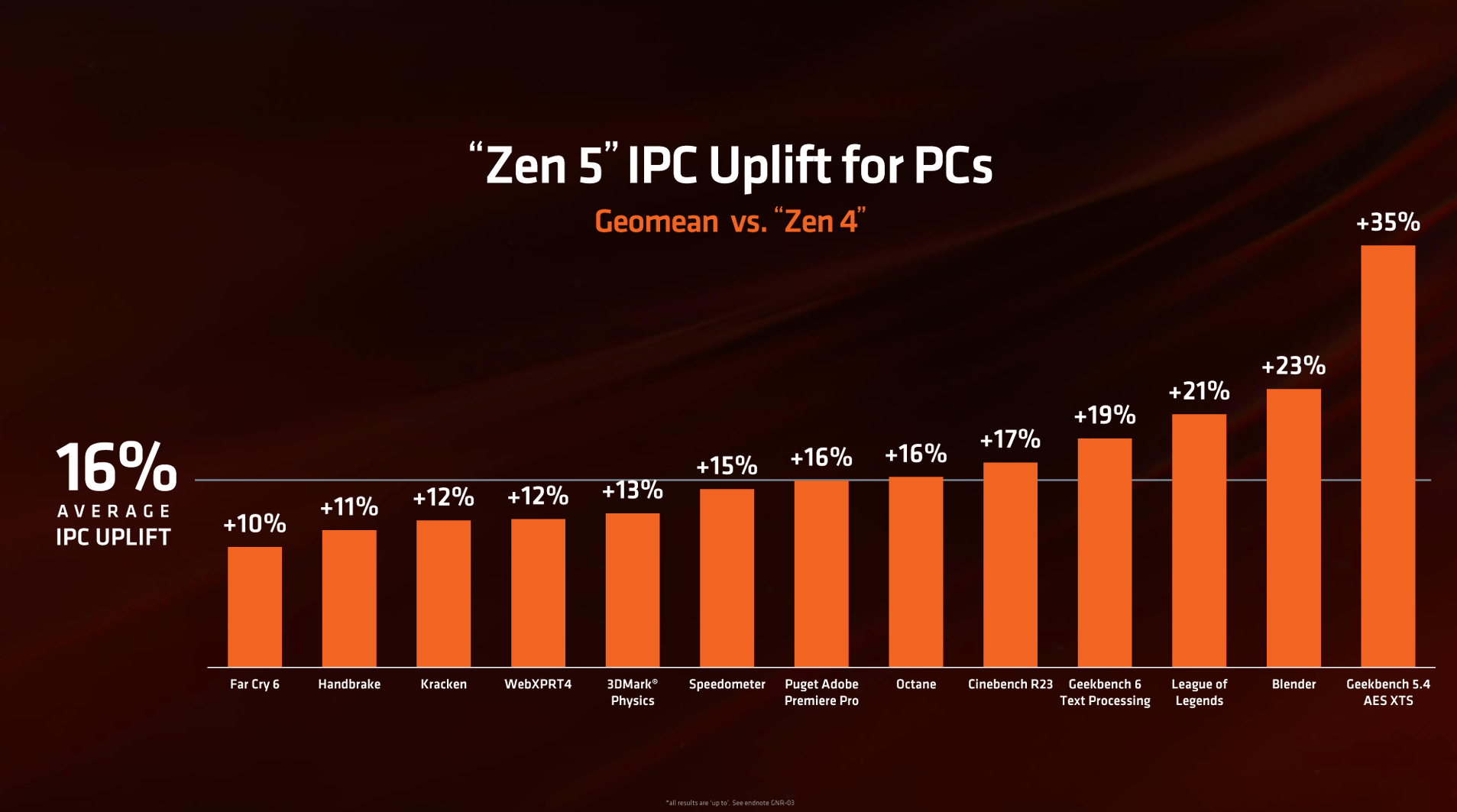
Zen 5 brings several key enhancements over its predecessor, Zen 4, focusing on performance and energy efficiency. One of the standout improvements is the 25% boost in performance per watt, allowing for more powerful processing while consuming less energy. Additionally, Zen 5 introduces a 16% increase in IPC (Instructions Per Cycle), meaning it can handle more work per clock cycle than Zen 4, leading to a smoother performance in demanding tasks.
Improvements have also been made in branch prediction and latency, ensuring faster and more efficient processing, especially in tasks that require quick decision-making or rapid data retrieval. The cache capacity has also significantly improved, with Zen 5-based Ryzen AI 300 processors offering 50% more on-chip memory than previous generations. This increased cache allows faster access to frequently used data, enhancing overall system speed and responsiveness.
Regarding power efficiency, the TDP (Thermal Design Power) of the Ryzen AI 300 series has been optimized to range between 15W and 54W, striking a balance between performance and power consumption. This optimization ensures that these processors are suitable for various devices, from energy-efficient laptops to more powerful desktops, without overheating or requiring excessive cooling.
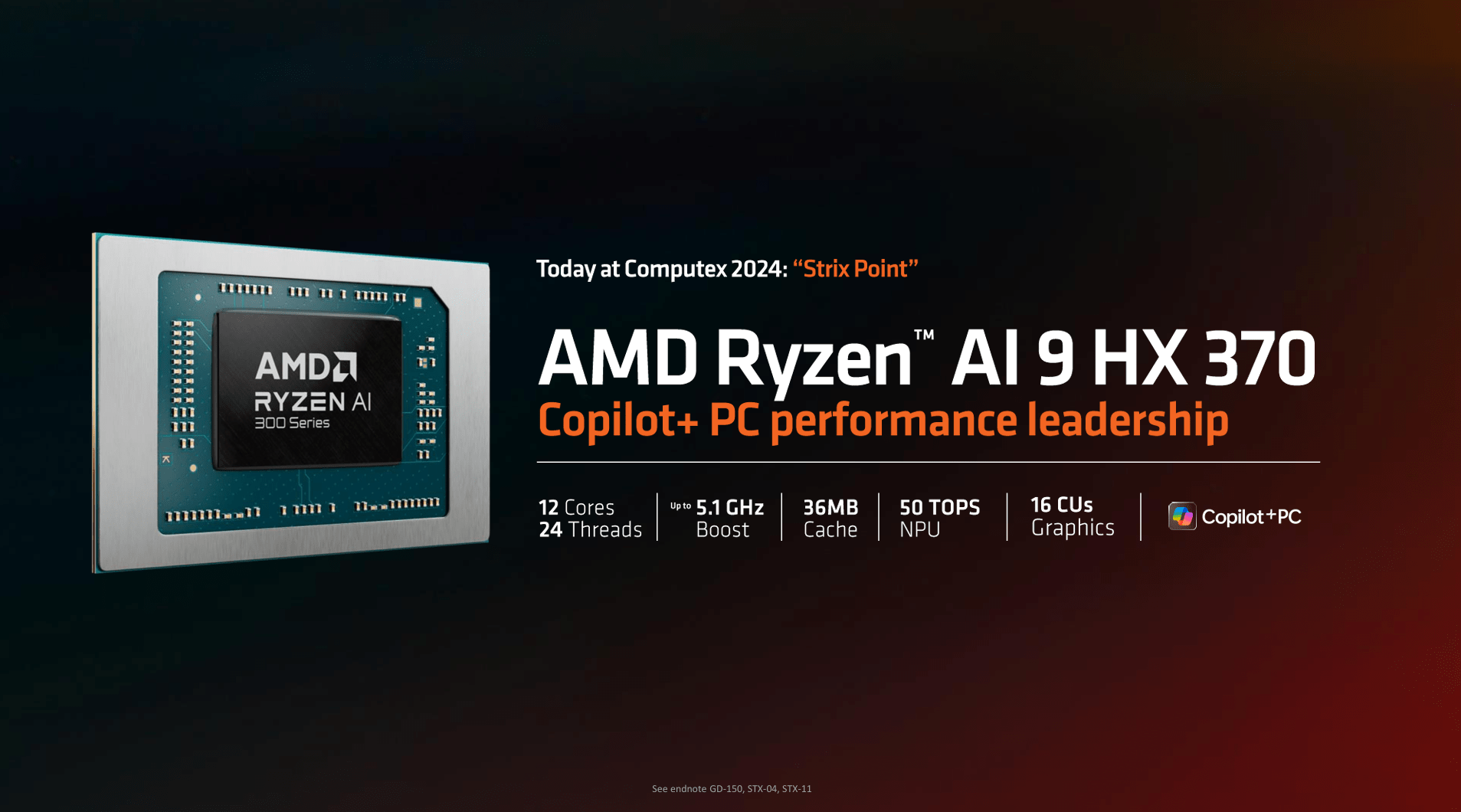
The Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 is the jewel in the crown.
The Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 is a high-performance processor featuring 12 cores and 24 threads, with a base clock speed of 2.0 GHz and a turbo boost up to 5.1 GHz. It combines 4 Zen 5 cores for high-demand tasks and 8 Zen 5c for energy-efficient operations, offering a well-rounded balance of power and efficiency.
Additionally, the processor boasts a 36 MB L3 cache and integrated Radeon 890M graphics, built on the RDNA 3.5 architecture. This makes it capable of handling intensive processing tasks and robust graphical workloads.
On the other hand, the Ryzen AI 9 365 is a slightly less powerful but still impressive option, featuring 10 cores and 20 threads. It operates at a base frequency of 2.0 GHz, with a turbo frequency reaching 5.0 GHz. This model also combines 4 Zen 5 and 6 Zen 5c cores, offering similar versatility between performance and energy efficiency. It includes a 24 MB L3 cache and integrated Radeon 880M graphics.
Both processors are equipped with the XDNA 2 NPU, delivering up to 50 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) of AI processing power, enabling advanced AI capabilities for various applications. These features make the Ryzen AI 9 processors adaptable to demanding tasks while maintaining excellent power efficiency.
RDNA 3.5 arrives on AMD Strix Point graphics cards
The AMD Strix Point processors bring integrated graphics based on the RDNA 3.5 architecture, offering a substantial leap in performance over the previous RDNA 3 generation. One of the most significant improvements is a 32% increase in performance per watt, making RDNA 3.5 more energy-efficient while delivering enhanced graphics capabilities.
Additionally, RDNA 3.5 includes optimizations in memory management and compression, which reduce memory access, further improving efficiency and overall performance.
For example, the Radeon 890M, integrated with the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370, represents a major upgrade over its predecessor, the Radeon 780M, which was included in processors like the AMD Ryzen 9 8840HS (used in the Acer Nitro Blaze 7). The Radeon 890M achieves 5.9 TFLOPS of computing power, a significant increase from the 4.3 TFLOPS of the Radeon 780M, offering enhanced graphics performance for gaming and demanding graphical tasks.
| Feature | Radeon 890M | Radeon 780M |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | RDNA 3.5 | RDNA 3 |
| Computing units | 16 | 12 |
| Shaders | 1024 | 768 |
| Maximum frequency | 2.9 GHz | 3.0 GHz |
| Theoretical performance | 5.9 TFLOPS | 4.3 TFLOPS |
| Ray Tracing | Yeah | Yeah |
| Energy consumption | 10-20 W | 35-54 W |
| Release date | June 2024 | January 2023 |
In contrast, the Radeon 880M, which comes with the Ryzen AI 9 365, delivers 4.5 TFLOPS. While still a powerful option, the 880M has fewer computing units, making it somewhat less potent than the 890M but still a solid choice for less graphically intensive applications.
The XDNA2 NPU joins the Copilot+ PC.
The XDNA 2 Neural Processing Unit (NPU) in the Ryzen AI 300 series is a key feature designed to excel at handling advanced AI workloads. With up to 50 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) processing power, it is well-equipped for real-time voice recognition, translation, and image/video enhancement. This represents a substantial leap over the previous generation, which maxed out at 16 TOPS.
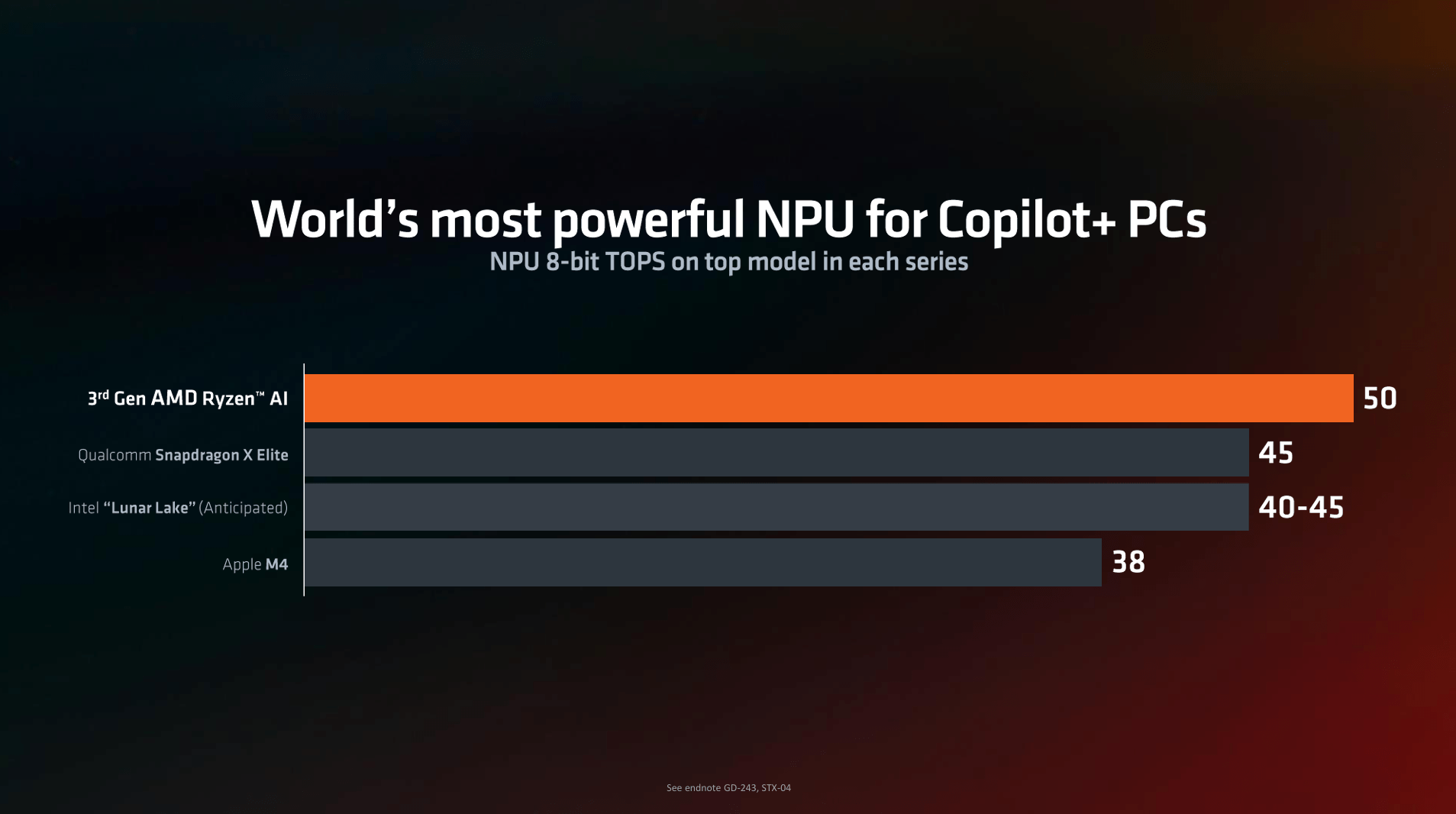
A major highlight is the improvement in power efficiency. The XDNA 2 NPU delivers five times the compute capacity at twice the energy efficiency compared to the NPU found in the Ryzen 7040 series.
How to understand the names of the Ryzen AI 300
AMD’s Ryzen AI 300 series features multiple SKUs tailored to different performance levels and price points. The model naming convention AMD uses follows a structured system to help users quickly understand key aspects of each processor.
- First figure: Indicates the processor generation.
- Second figure: Represents the performance segment (9 for high performance, 7 for medium-high performance, 5 for medium performance).
- Third figure: Differentiate models within the same segment.
- HX Label: Indicates that the processor is optimized for high performance.

| Model | Cores | Threads | Base Frequency | Turbo frequency | L3 Cache | Integrated Graphics | NPU (TOPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 | 12 | 24 | 2.0 GHz | 5.1 GHz | 36 MB | Radeon 890M | 50 |
| Ryzen AI 9 365 | 10 | 20 | 2.0 GHz | 5.0 GHz | 24 MB | Radeon 880M | 50 |
| AMD Ryzen AI PRO 360 | 8 | 16 | 2.0 GHz | 4.8 GHz | 24 MB | Radeon 880M | 50 |
AMD Strix Point Availability and Equipment
AMD’s Ryzen AI 300 processors will start appearing in a wide range of mobile devices from Q4 2024, with major brands like HP, Lenovo, and Acer already planning to integrate these processors into their upcoming laptop lines. Alongside the larger manufacturers, smaller brands are also innovating with new device form factors powered by AMD Strix Point processors.
Notably, there will be a dual-screen laptop from GPD called the Duo and a compact Mini-PC from Minisforum named the EliteMini AI370. These developments signal a diverse range of devices leveraging the advanced AI and performance features of the new Ryzen chips.