Microsoft Excel is a popular spreadsheet application for editing, analysing, and storing numerical data in a structured format. It offers various formulas and functions that help perform various calculations, making it an essential business tool.
However, like any software, Excel isn’t free from errors. Many users have reported encountering different errors while working with Excel spreadsheets. Some of these issues are minor and can be resolved quickly, but others, such as the common ‘Runtime Error 1004,’ can be more challenging to fix.
What is runtime error 1004 in Excel?
When using Excel, if you try to run VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), create a macro, or modify range values, you might encounter the ‘Runtime Error 1004.’ This error can also occur when there are too many legend entries but insufficient space in the Excel sheet to accommodate them.
The error can be triggered by issues such as file conflicts, a corrupted Excel file, data mismatches, or an incorrect macro name. Since this error can potentially lead to data loss or file corruption, resolving it promptly to protect your data is essential.
Possible reasons for runtime error 1004 in Excel
Various issues can cause Runtime Error 1004 in Excel. Here are some common reasons:
- Corrupt or Invalid Data: If your spreadsheet contains corrupt or invalid data, trying to perform operations on this data can lead to errors.
- Issues with VBA Code or Macros: Errors in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) code or improper syntax while creating or running macros can trigger Runtime Error 1004.
- Compatibility Issues: The error may arise due to compatibility problems between different versions of Excel or conflicts with installed add-ins or plugins.
- Insufficient Memory or System Resources: If your system lacks the necessary memory or resources to perform operations in Excel, you might encounter this runtime error.
- Conflicting Plugins or Applications: Third-party add-ins or applications installed in Excel can cause conflicts, especially if they have compatibility issues or overlapping functions, leading to the error.
- Logical or Syntax Errors in Code: Incorrect syntax or logical errors in VBA code can cause failures when writing or modifying macros, resulting in Runtime Error 1004.
Identifying the specific cause of the error is crucial for effectively troubleshooting and resolving it. Each of the above issues requires a different approach to fix the underlying problem.
Methods to fix runtime error 1004 in Excel
Different methods can be used depending on the cause of the error. Below are the methods to rectify runtime error 1004:
1. Check macros
If you encounter runtime error 1004 while running a macro in Excel, try reviewing the code for any mistakes, such as syntax errors, missing references, or invalid operations. Go through the code step by step to identify and correct any issues.
Usually, by checking the code and making the needed adjustments, you can resolve the problem.
You can check the Macro Code by following the steps below:
- Start the Excel workbook that contains the macro to be checked.
- Now open the VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) editor by clicking Alt+F11 on your keyboard.
- In the VBA editor, locate the Project Explorer window (on the left side of the screen), which contains a list of workbooks and module names.
- Click on the plus sign (+) next to the workbook containing the Macro Code you want to check. This will display the modules in the workbook.
- Now, double-click on the module to view the macro code you want to check. The code editor window containing the code will open.
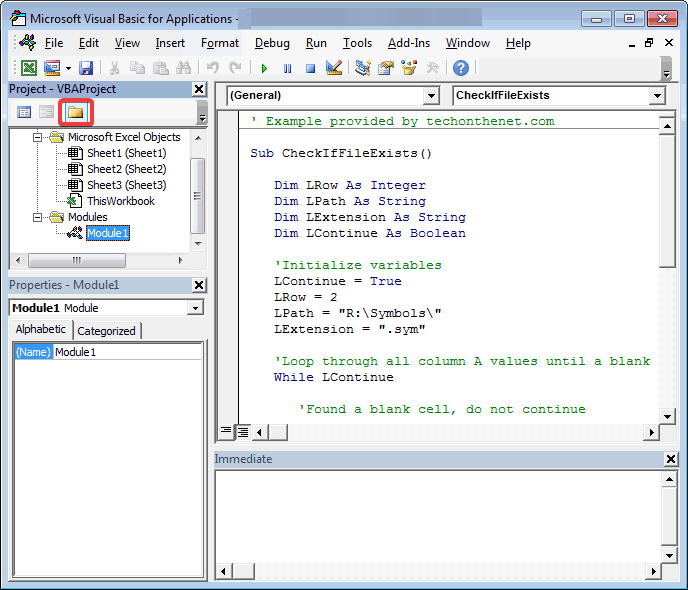
- To start checking the macro code, place the cursor at the beginning or on the line from which you want to check the code.
- You can scroll through the code line by line with the cursor or press the key. Press F8 from your keyboard to use the shortcut.
- The codes appear highlighted (the code to be executed and also the next line for execution).
- You can continue pressing F8 to step through the code line by line. You will notice the variables in the values and the program sequence.
- To skip a code section without checking each line, set a breakpoint in the code. To do this, click the grey border to the left of the line where you want to set the breakpoint.
- A red dot indicates the breakpoint. If you now run the macro (after setting the breakpoint) and execute the code, the action stops at the breakpoint so that you have time to check the code from this point onwards.
- If you check the code and see an error message in the VBA editor, take note of the line number and the error message. You can use this information for troubleshooting purposes.
Note: If you check macros in the VBA editor, you can examine the logic, variables, and operations performed by the macro. This helps you recognize code errors and makes it easier to improve the code.
2. Uninstall Microsoft Work
Sometimes, runtime error 1004 in Excel can happen because of a conflict between Microsoft Works and Microsoft Excel. This issue is more common if you’re using Excel 2009 or an earlier version. If both programs are installed on your computer, uninstalling Microsoft Works can help resolve the error.
To uninstall Microsoft Work, follow the steps below:
- Open your system’s control panel.
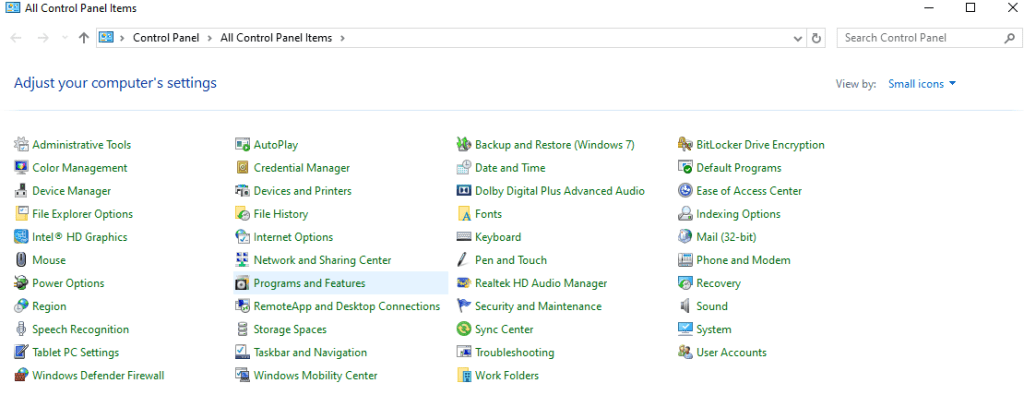
- Select programs and functions.
- In the Programs and Features window, look for Microsoft Work in the list of programs installed on your system.
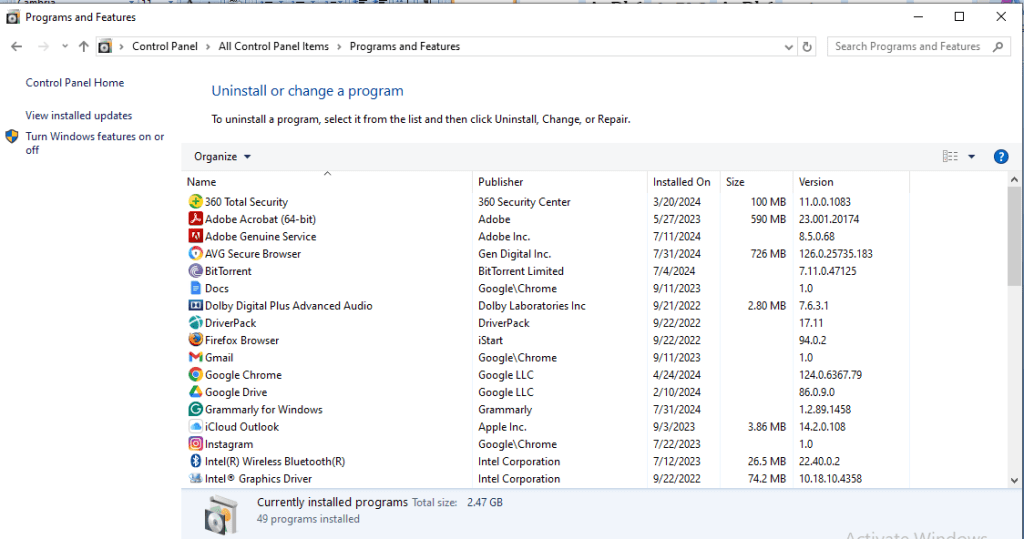
- Now click on Uninstall and follow the on-screen instructions to remove the program from your computer.
3. Delete GWXL97.XLA files
GWXL97.XLA is an MS Excel add-in file that provides additional functionality for the Excel spreadsheet. Sometimes, the add-in file conflicts with Excel and triggers a runtime error 1004. The problem can be fixed by simply deleting the existing GWXL97.XLA files.
Follow the step-by-step instructions to remove GWXL97.XLA plugin files.
- Go to the Excel startup folder, usually in C:\Program Files\NMicrosoft Office\NOffice\XLSTART.
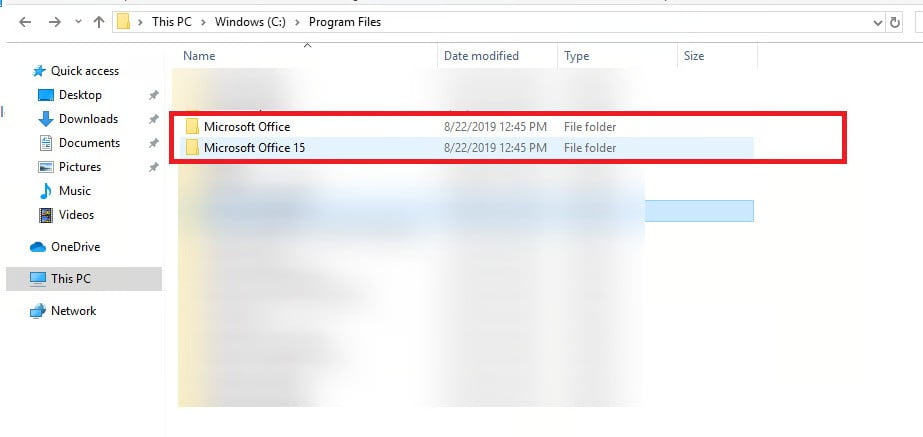
- Look for the GWXL97.XLA files in this folder.
- Now select the files and delete them.
- You can restart Excel and check if the error has been rectified.
4. Change Trust Centre Settings
If Microsoft Excel security settings are not configured correctly, it can cause runtime error 1004. You can adjust these settings by accessing the Trust Centre in Excel, where you can manage privacy and security options.
Perform the following steps to change the trust centre settings:
- Start MS Excel.
- Now go to «Archive» and click on «Options» in Excel.
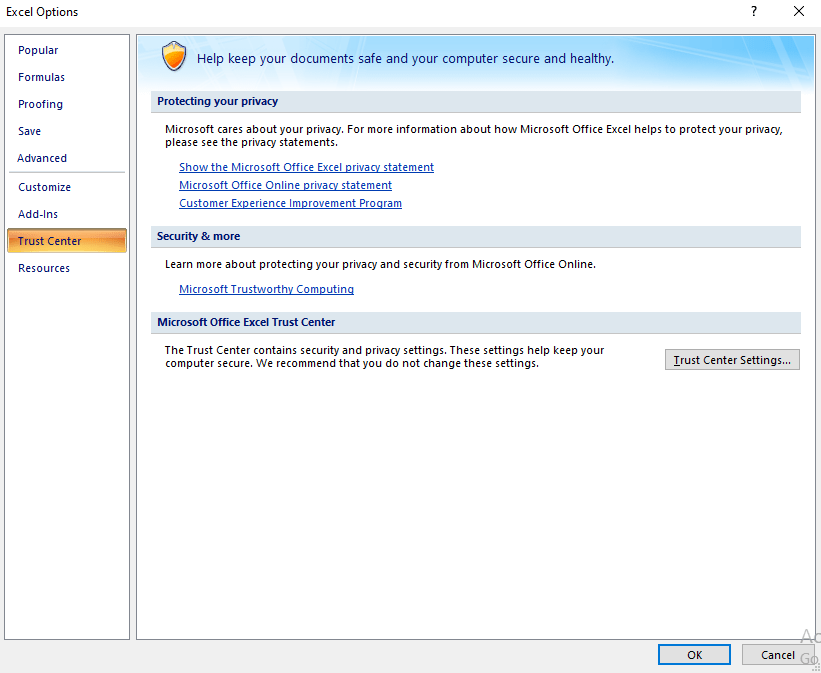
- The window “Excel Options. «
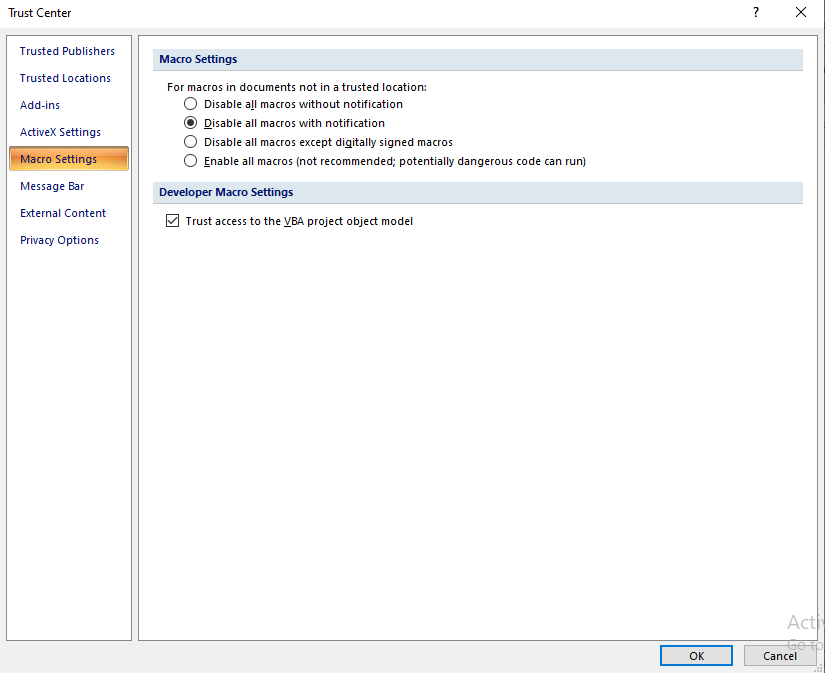
- Click «Trust Centre» in the left bar and then «Configuring the Trust Centre» in the window on the right.
- Go to the ‘ tabMacro Settings’ in the left bar. In the expanded window, in ‘Setting up macros for developers‘, check the box before ‘Trust access to the VBA project object model‘.
- Then press OK.
5. Use the Open and Repair Tool in MS Excel
When Microsoft Excel detects a corrupted worksheet, it may cause runtime error 1004 to occur. Typically, Excel will automatically initiate data recovery mode to try and repair the file. If this doesn’t happen, you can manually use Excel’s built-in “Open and Repair” tool to fix the file.
- Open Microsoft Excel, go to «Archive» and click on «Open«.
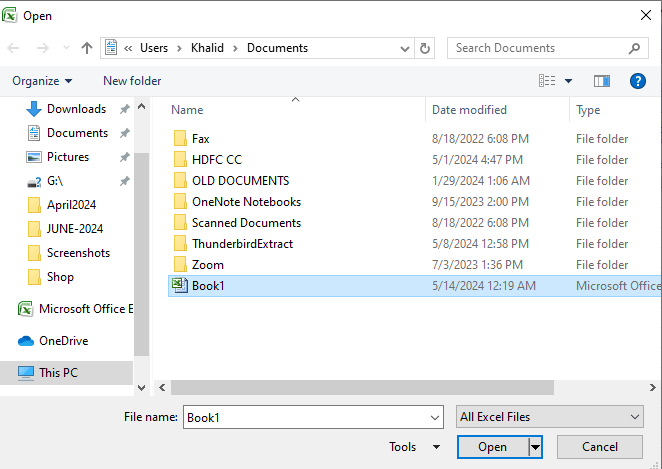
- In the dialog box, Open navigate to the folder where the damaged workbook is located.
- Now select the damaged book.
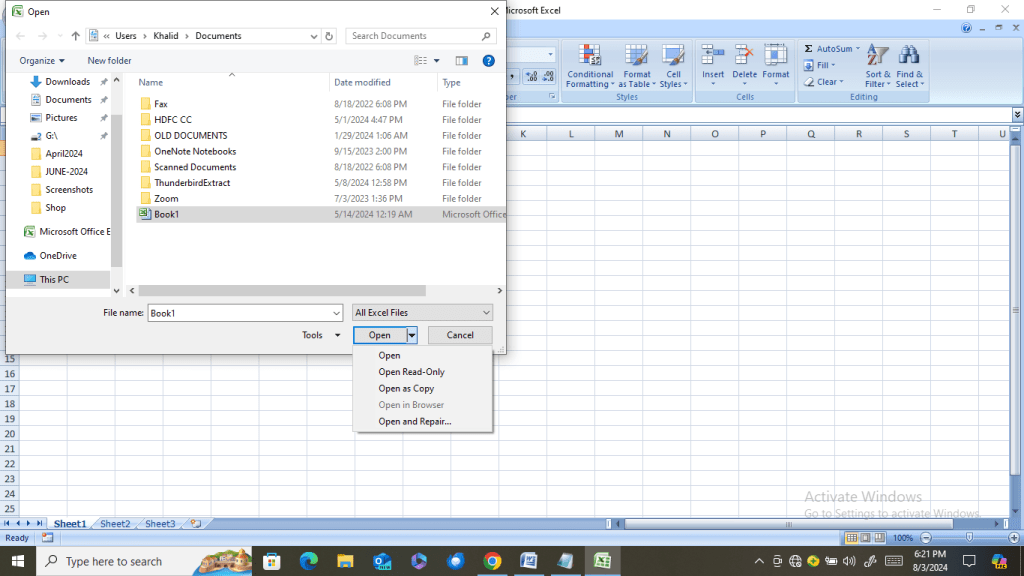
- Click the arrow next to the Open button and select the option Open and repair.
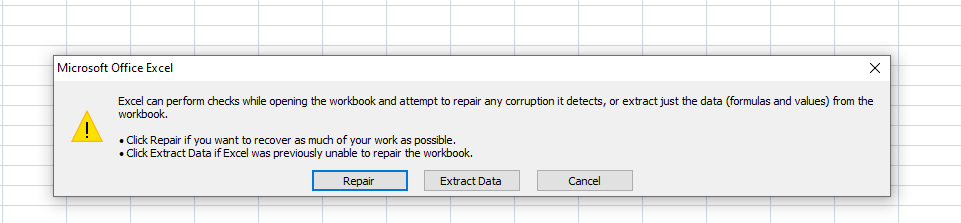
- If prompted, click the Fix option.
Excel runtime error 1004 can occur during program execution for various reasons, which we’ll explore in this article. We’ll also cover different methods to fix this error.
If the error is due to a corrupt Excel file, you can try using Excel’s built-in “Open and Repair” tool. This tool works well for minor corruption issues. For more severe corruption, you might need third-party software like Stellar Repair for Excel. This advanced tool can handle all Excel file problems, recover data from corrupt files, and save it in a new workbook.