Reverse image search has become an essential tool in the modern digital landscape. In an era dominated by visuals, this technology allows users to search the web using an image instead of text, uncovering where it originated, where else it appears, and how it may have been used or altered. Whether you’re verifying social media photos, checking for copyright infringement, or finding product information, reverse image search reveals what words often can’t describe.
By 2025, advances in AI-powered visual recognition and content-based image retrieval (CBIR) have made this process faster, more intelligent, and far more accurate. Today’s tools not only find identical pictures but can recognise similar patterns, objects, and contexts—even in cropped or filtered versions.
What Is Reverse Image Search?
Reverse image search is a visual data retrieval method that allows you to perform a search by uploading or pasting an image instead of typing a query. It forms the foundation of how modern visual search engines and AI recognition systems operate.
Powered by CBIR (Content-Based Image Retrieval) technology, reverse image lookup analyses specific features within an image—such as colour distribution, texture, geometry, and embedded data—to find visually related matches online. It eliminates the trial-and-error of guessing text-based keywords and delivers visually similar or exact matches from global image databases.
This technology is used across industries: journalists verify photo authenticity, photographers track image plagiarism, brands monitor misuse of their assets, and everyday users detect fake profiles or manipulated images on social networks.
- Prepare your image by saving it in a supported format such as JPG, PNG, or WebP.
- Choose a reverse image search engine (Google Images, Yandex, Bing, or TinEye).
- Upload your image or paste the image URL.
- Wait as the system analyses and compares it with its database.
- Review the results, including visually similar images, source websites, and metadata details.
Reverse image search transforms visual information into searchable data, helping uncover an image’s story, authenticity, and digital footprint across the web.
How to Do the Visual Search Using Search Engines
Google Lens (AI-Enhanced Visual Search)
Google Lens represents the next generation of reverse image search. Integrated across Android, Chrome, and Google Photos, it goes beyond basic image matching by understanding context and identifying the real-world elements within a picture.
Google Lens uses machine learning and neural vision models to recognise faces, products, places, and even text inside images. Unlike traditional reverse search, it doesn’t just show “similar pictures” — it provides detailed insights, such as shopping results, map locations, or translation for visible text.
Steps:
- Open Google Lens on your phone via the Google Photos app or in Chrome.
- Upload or capture the image you want to search.
- Highlight the area of interest (face, object, or text).
- Review AI-generated results, including related web pages, products, or original sources.
For users seeking quick, intelligent, and context-aware results, Google Lens is the best option in 2025, combining image recognition with AI-driven search precision.
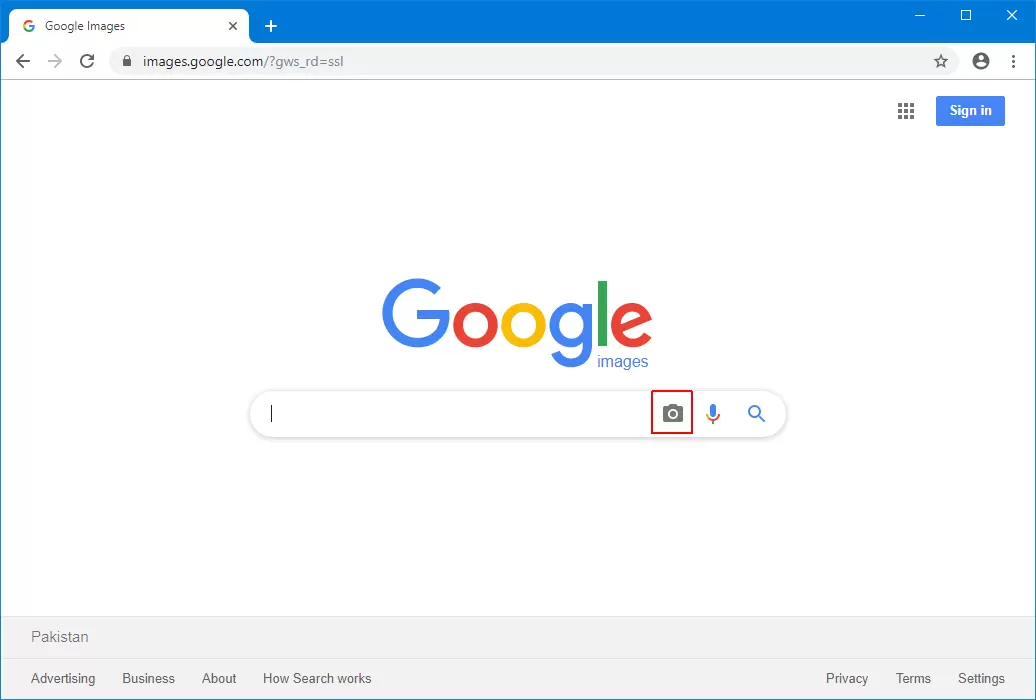
Google Images Classic Reverse Search
The classic Google Images reverse search tool remains a favourite for desktop users who prefer a straightforward and reliable method.
This service allows you to upload an image or paste its link into Google’s search bar. Google then scans billions of indexed web pages to locate duplicates, similar versions, or modified copies. It’s a simple yet powerful solution for image verification, source tracking, and content authenticity.
Steps:
- Visit images.google.com.
- Click the camera icon in the search bar.
- Select “Paste Image URL” or “Upload an Image.”
- Analyse the returned results showing matching visuals and source websites.
Google Images continues to be a top-tier reverse image search engine due to its enormous database, making it ideal for verifying images and finding duplicates quickly.
Bing Visual Search
Microsoft’s Bing Visual Search has evolved into a highly capable AI-based visual lookup tool integrated with the Edge browser and Microsoft Copilot.
Bing Visual Search identifies not only direct matches but also contextually similar images by studying colours, shapes, and object relationships. It excels in commercial searches—helping users find products, designs, or logos through visual comparison.
Steps:
- Navigate to bing.com/images.
- Click on the Visual Search (camera) icon.
- Upload your image or paste its URL.
- Review search results featuring similar products, images, and web pages.
With its enhanced AI analysis, Bing Visual Search offers excellent accuracy and object recognition, making it a practical tool for e-commerce and brand image discovery.
Yandex Image Search
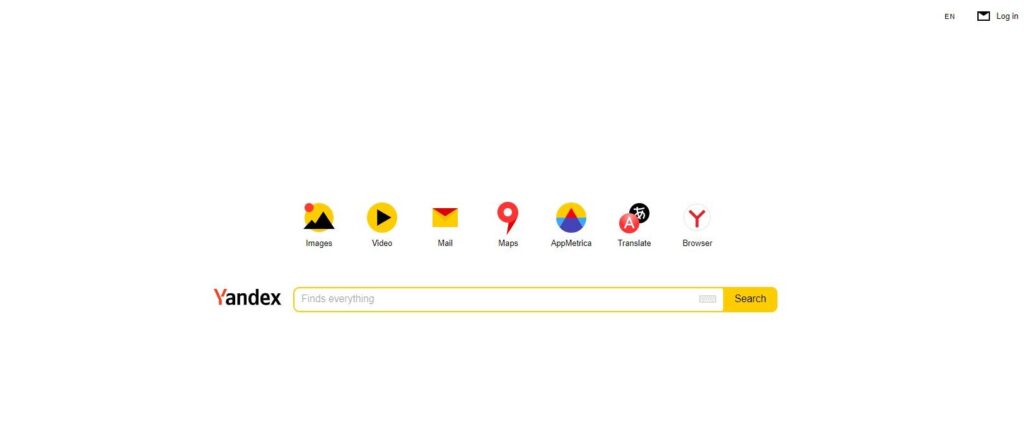
Yandex Images, Russia’s largest visual search platform, provides broader international coverage and excels in finding people, places, and rare visuals often missed by Western search engines.
Yandex’s CBIR engine detects image similarities based on structure, tone, and facial mapping. It’s a go-to platform for identifying social media photos, digital art, or images circulating in Eastern Europe and Asia.
Steps:
- Go to yandex.com/images.
- Click the camera icon.
- Upload or paste your image link.
- Browse through matched results, including regional sources and duplicates.
Yandex remains an invaluable alternative for global reverse image searching, especially for users investigating content beyond mainstream Western platforms.
TinEye Image Tracker
TinEye is a professional-grade reverse image tracking platform specialising in monitoring where and how images appear online.
TinEye employs a unique “image fingerprinting” technology that recognises even resized, rotated, or colour-edited images. Unlike standard search engines, it focuses solely on image data, not keywords or metadata, making it one of the most accurate tools for copyright monitoring.
- Visit tineye.com.
- Upload your image or paste its URL.
- TinEye scans its massive database for identical and derivative versions.
- Review results showing all sites where the image appears, including timestamps.
For photographers, designers, and brands protecting intellectual property, TinEye remains the most trusted reverse image tracking solution.
Face Recognition Search Engines
The rise of fake accounts and identity theft has created the need for specialised face recognition search engines.
Platforms such as PimEyes, FaceCheck.ID, and Betaface use advanced facial mapping algorithms to match faces across the web. These tools help verify social media identities, detect impersonation, or locate online appearances of the same individual.
Steps:
- Visit a face recognition search engine like PimEyes.
- Upload a clear, front-facing image.
- Allow the tool to analyse and compare the face against its indexed images.
- Review the list of potential matches or identical profiles found online.
Facial recognition search tools are powerful verification resources. When used responsibly, they can expose fake accounts and confirm online identities effectively.
AI-Powered Reverse Search Apps
Mobile users can now access AI-driven reverse image search apps that integrate multiple search engines in one place.
Applications such as CamFind, Reversee+, and Search by Image Pro use deep learning to detect objects, people, or logos and perform simultaneous searches across Google, Bing, and Yandex databases.
Steps:
- Install a trusted reverse image search app from the Play Store or App Store.
- Upload or capture the image directly through the app.
- The AI automatically searches multiple engines.
- Check the summarised results with image sources and related pages.
These all-in-one mobile tools make visual search more convenient for users who need instant verification while browsing or shopping.
Metadata and EXIF Data Analysis
Beyond visual analysis, examining an image’s hidden information—known as metadata—can reveal its origin and authenticity.
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data contains embedded details like capture date, camera model, GPS location, and editing history. Analysts use this information to validate when and where a photo was taken, or to detect possible tampering.
Steps:
- Upload your image to an EXIF reader such as ExifTool or ImageForensics.io.
- Review embedded data like date, location, and software used.
- Use this data to support or refine your reverse image search findings.
Metadata analysis provides deeper verification by exposing details invisible to the eye, strengthening the accuracy of visual investigations.
Reverse image search in 2025 is more powerful, intelligent, and accessible than ever. With AI, computer vision, and machine learning now driving major platforms like Google Lens, Bing, Yandex, and TinEye, users can trace the origin of any photo, verify authenticity, detect edits, and safeguard their digital presence.
From confirming the legitimacy of social media profiles to protecting creative content from theft, reverse image search tools empower individuals and professionals alike to ensure that every picture tells the truth.
Whether used for image verification, copyright protection, or digital investigation, mastering these modern visual search methods keeps you informed, secure, and one step ahead in an image-driven online world.